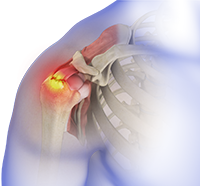
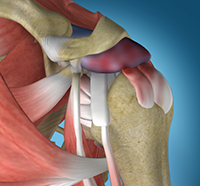
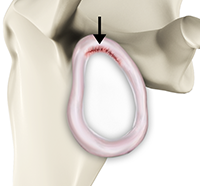
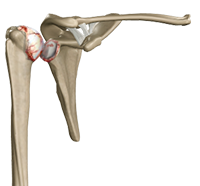
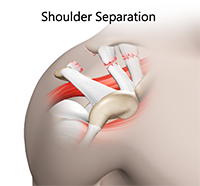
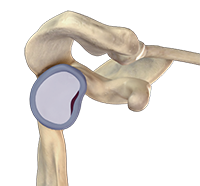
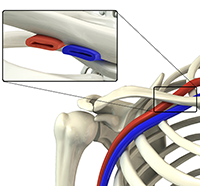
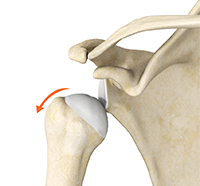
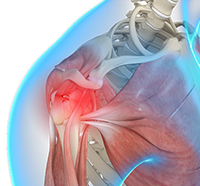
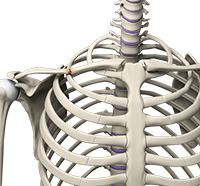
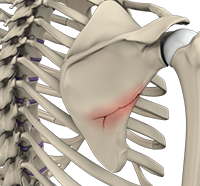
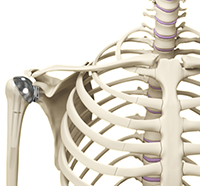
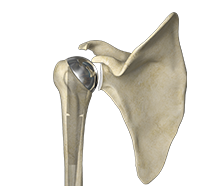
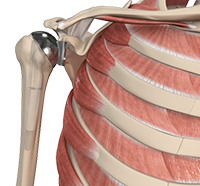
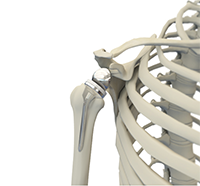
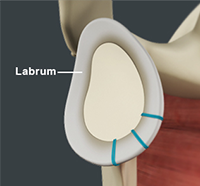
The shoulder is the most flexible joint in the body enabling a wide range of movements including, forward flexion, abduction, adduction, external rotation, internal rotation, and 360-degree circumduction. Thus, the shoulder joint is considered the most insecure joint of the body but the support of ligaments, muscles and tendons function to provide the required stability





 Dr. MJW (Collie) Begg
Dr. MJW (Collie) Begg Dr. Nicholas M. Chabrel
Dr. Nicholas M. Chabrel Dr. Andrew S. Comley
Dr. Andrew S. Comley Dr. Basel Masri
Dr. Basel Masri Dr. Michael J. Sandow
Dr. Michael J. Sandow Dr. Chen Tu
Dr. Chen Tu Dr. Arthur Turow
Dr. Arthur Turow